
Super Early Strength Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer For Sleeve Grouting Material
Blog Super Early Strength
Blog

Abstract: In the continuous development of concrete technology, water reducing admixtures play a crucial role as additives in improving concrete performance.
A deep understanding of the types, characteristics, and applications of water reducing agents has profound significance for optimizing concrete mix design, improving engineering quality, and promoting sustainable development in the construction industry.
Ligninesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt is produced by concentrating sulfite papermaking pulp waste liquid and using precipitants such as lime, calcium chloride, and basic lead acetate through precipitation, separation, and drying.
Lignosulfonate is a linear polymer compound soluble in aqueous solutions of various pH values and insoluble in organic solvents. Its functional group is phenolic hydroxyl. Usually, it is a yellow-brown solid powder or viscous slurry. Has good diffusivity and is easily soluble in water.
Water reduction rate: The water reduction rate of lignin-based water-reducing agents is relatively low, generally around 10% -15%. This means that using lignin-based water-reducing agents in concrete can reduce water consumption to a certain extent. Still, their water-reducing effect is limited compared to other high-efficiency water-reducing agents.
Delaying effect: This type of water reducing admixtures has a significant retarding effect. This is because functional groups such as hydroxyl groups in lignin molecules can undergo complexation reactions with calcium ions on the surface of cement particles, delaying the hydration process of cement. In some projects that require longer construction time or construction in high-temperature environments, this retarding effect may be advantageous. Still, in projects with strict requirements for setting time, caution may be needed when using it.
Air entraining property: Lignin-based water reducers usually introduce a certain amount of tiny bubbles into the concrete, thereby increasing its air content. Moderate air entrainment can improve the frost resistance and workability of concrete. Still, excessive air entrainment may lead to a decrease in concrete strength.
Ligninesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt are suitable for projects that do not require high concrete strength, have long construction times, or have specific requirements for concrete frost resistance.
For example, the strength grade requirements for concrete in the foundation construction of some small civil buildings are relatively low, and the construction process may be relatively slow. Lignin-based water reducers can meet these requirements, and their air-entraining properties help improve the frost resistance of concrete during winter construction.
In addition, in constructing base concrete in some road projects, lignin-based water reducers can also be used to improve the workability and frost resistance of concrete.
Naphthalene-based water-reducing agents are synthesized from industrial naphthalene, the primary raw material, through chemical reactions such as sulfonation, hydrolysis, and condensation.
It is a non-air-entraining water-reducing agent. This means that naphthalene-based water-reducing agents will not produce bubbles in the concrete, thus not affecting its internal structure.
Water reduction rate performance: The water reduction rate of naphthalene-based water reducers is significantly higher than that of lignin-based water reducers, usually reaching 15% -25%. This allows for a certain degree of reduction in the cement ratio in concrete mix design, thereby improving the strength of concrete.
Poor slump retention ability: However, the slump retention ability of naphthalene-based water reducers is relatively poor. Within a certain period after concrete mixing, the slump will quickly decrease, which requires stricter control of the transportation and pouring time of concrete during the construction process or additional measures to maintain the slump, such as adding water-reducing agents twice at the construction site.
Adaptability to cement: There are specific differences in the adaptability of naphthalene-based water reducers to different types of cement. Some types of cement may be poorly compatible, leading to unstable workability or abnormal strength development of concrete.
Water reduction rate performance: The water reduction rate of naphthalene-based water reducers is significantly higher than that of lignin-based water reducers, usually reaching 15% -25%. This allows for a certain degree of reduction in the cement ratio in concrete mix design, thereby improving the strength of concrete.
Poor slump retention ability: However, the slump retention ability of naphthalene-based water reducers is relatively poor. Within a certain period after concrete mixing, the slump will quickly decrease, which requires stricter control of the transportation and pouring time of concrete during the construction process or additional measures to maintain the slump, such as adding water-reducing agents twice at the construction site.
Adaptability to cement: There are specific differences in the adaptability of naphthalene-based water reducers to different types of cement. Some types of cement may be poorly compatible, leading to unstable workability or abnormal strength development of concrete.
Naphthalene-based water-reducing agents are widely used in industrial and civil construction, especially in ordinary concrete engineering.
For example, in constructing concrete structures in multi-story residential buildings, naphthalene-based water-reducing agents can effectively improve the strength of concrete and meet the design requirements of building structures.
In some general industrial plant construction, there are specific requirements for the strength and workability of concrete, and naphthalene-based water reducers can also play a good role. However, in some projects that require high workability of concrete, such as cantilever pouring construction of large bridges or pumping concrete construction of high-rise buildings, the use of naphthalene-based water reducers alone may not meet the requirements and needs to be combined with other additives.
It is the product of sulfonating melamine with sulfuric acid and condensation with formaldehyde; hence, the chemical name sulfonated melamine formaldehyde resin. It belongs to the anionic surfactants family.
This type of water reducing agent has a white powder appearance, is easily soluble in water, disperses the powder material well, has a high water reduction rate, and has good fluidity and self-healing properties.
High water reduction rate characteristics: Melamine-based water-reducing agents have a high water reduction rate, reaching 20% -30% or even higher. This enables concrete to maintain good workability even at lower water-cement ratios, significantly improving its strength and durability.
Early strength development: This type of water reducer can promote cement’s early hydration reaction, speeding up concrete’s early strength development. This is significant for some projects requiring rapid demolding or early load-bearing, such as producing prefabricated concrete components and bridge repair.
Durability improvement: Due to their excellent water-reducing effect and optimization effect on the microstructure of cement hydration products, melamine-based water-reducing agents can help improve concrete durability indicators such as impermeability and chemical resistance and extend the service life of concrete structures.
Melamine water reducer are suitable for projects requiring high strength and durability of concrete and for producing prefabricated components requiring rapid construction.
High requirements are placed on concrete’s strength, durability, and early strength in building bridges on highways. Melamine-based water reducers can meet these requirements, ensuring the safety and durability of bridge structures.
Using melamine water reducer to produce prefabricated concrete beams, slabs, columns, and other components can shorten the production cycle, improve mold turnover, and reduce production costs. However, the production cost of melamine-based water-reducing agents is relatively high. A certain amount of harmful substances, such as formaldehyde, are generated during production, limiting their wider application.
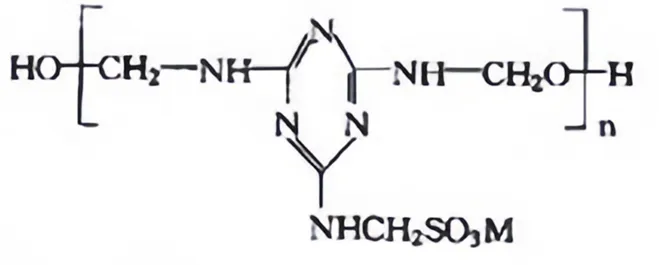
The chemical name is aromatic aminosulfonate polymer, produced from sodium p-aminobenzenesulfonate and phenol as raw materials through addition and condensation reactions to ultimately form a polymer with a certain degree of polymerization.
The molecular structure of amino sulfonic acid-based high-efficiency water-reducing agents is relatively complex, and different monomers will have different molecular structures. However, the widely recognized structural formula of these agents is shown in the figure.

Water reduction and slump retention performance: Amino sulfonate-based water-reducing agents have a high water reduction rate, usually around 20% -30%, and good slump retention ability. For a long period after concrete mixing, it can effectively maintain the slump of concrete and reduce slump loss, which is very beneficial for concrete projects that require long-distance transportation or construction in high-temperature environments.
Slow setting effect and adaptability: This type of water reducing admixtures has a specific slow setting effect, but its slow setting degree is relatively mild, unlike lignin-based water reducers, which are as strong. In addition, the amino sulfonate-based water-reducing agent is adaptable to cement, and its performance is relatively stable in different types of cement, which can effectively reduce water and retain slump.
Aminosulfonic acid based superplasticizer are suitable for large-volume concrete projects, projects constructed in high-temperature environments, and projects that require high workability and durability of concrete.
Due to the massive amount of concrete, long construction period, and construction in high-temperature environments in summer, amino sulfonate water-reducing agents can effectively control the slump loss of concrete, reduce the temperature rise of hydration heat, and prevent the occurrence of concrete cracks in the concrete construction of large water conservancy hub projects.
Polycarboxylate superplasticizer is a type of polymer admixture, a composite product of carboxylic acid grafted copolymers and other effective additives. Its molecular structure is mainly composed of a main chain and side chains. The main chain usually contains strong polar groups, such as carboxyl and sulfonic acid groups, which are connected to the polyoxyethylene side chains through chemical bonds.
The side chains of polyethylene oxide have different lengths and degrees of polymerization, and their structural characteristics endow polycarboxylate superplasticizers with unique properties. The molecular weight distribution of polycarboxylate superplasticizers is relatively narrow, and the molecular structure can be designed and adjusted according to different engineering requirements.
High water reduction and slump retention synergy: Polycarboxylate-based water-reducing agents have incredibly high water reduction rates, reaching 30% -40% or even higher. In contrast, their slump retention ability is excellent. Within a few hours after concrete mixing, the slump loss is minimal, which can meet the high requirements for concrete workability, such as long-distance transportation, pumping construction, and complex structural pouring.
Molecular structure designability: Polycarboxylate superplasticizers with different performance characteristics can be customized by changing parameters such as the type and quantity of functional groups in the molecular structure and the length of the polyoxyethylene side chain. For example, increasing the number of carboxyl groups can improve the water reduction rate, and extending the length of the polyoxyethylene side chain can enhance the slump resistance, thereby meeting concrete performance requirements under various special engineering conditions.
Environmental friendliness: Polycarboxylate water reducers do not use harmful substances such as formaldehyde in production, which meets environmental protection requirements. They will not release toxic gases during the use of concrete and are harmless to the environment and human health. They are a green and environmentally friendly additive.
Comprehensive improvement of concrete performance: This type of water reducer can not only enhance the strength and durability of concrete but also improve its various properties, such as impermeability, frost resistance, and chemical resistance. At the same time, it has a good optimization effect on the microstructure of concrete, making it denser and reducing porosity, thereby improving the overall quality of concrete.
Polycarboxylate-based water-reducing agents are widely used in high-performance concrete engineering, such as superhigh-rise buildings, large-span bridges, high-speed railways, marine engineering, etc.
Pumping equipment must transport concrete to extremely high floors in superhigh-rise buildings. Polycarboxylate superplasticizers’ high water reduction rate and good collapse resistance ensure the permeability and workability of concrete. In contrast, their high strength and durability guarantee the safety of building structures.
In large-span bridge engineering, polycarboxylate superplasticizers can improve concrete’s crack resistance and durability and withstand long-term vehicle loads and natural environmental erosion.
In marine engineering, faced with seawater erosion and harsh aquatic environments, polycarboxylate superplasticizers can enhance the impermeability, resistance to chloride ion penetration, and resistance to chemical erosion of concrete, extending the service life of marine structures.

The primary raw materials for producing aliphatic water-reducing agents are acetone and formaldehyde Na2SO3、Na2S2O5、 Catalysts, etc. A brownish-red liquid product with a concentration of 30% to 40%, with a water reduction rate of up to 20%, can be used for low-grade concrete and will cause staining of the concrete.
Its molecular structure contains functional groups such as carbonyl and sulfonic acid groups. The main chain of the molecule is usually an aliphatic carbon chain structure, which has a certain degree of flexibility. The molecular weight of aliphatic water-reducing agents is generally between several thousand and tens of thousands, and the molecular structure is relatively simple.
Water reduction and reinforcement effect: Aliphatic superplasticizer have a specific water reduction rate, usually around 15% -25%, which can reduce the water-cement ratio to a certain extent and improve the strength of concrete. At the same time, it has a good strengthening effect on concrete in both early and late stages, promoting the hydration reaction of cement and continuously increasing its strength.
Adaptability and cost advantages: This type of water reducer is adaptable to cement and has relatively stable performance for different kinds of cement. In addition, the production cost of aliphatic water-reducing agents is relatively low, which has certain economic advantages and application potential in some cost-sensitive projects.
Effects of air entrainment and setting time: Aliphatic water reducers may introduce some bubbles during use. However, their air entrainment effect is relatively weak, and their impact on concrete strength is relatively small. At the same time, they have a relatively small impact on the setting time of concrete and generally do not cause it to be too long or too short.
Aliphatic superplasticizer are suitable for general industrial and civil construction projects, such as ordinary residential buildings, factory construction, etc. Some ordinary multi-story residential buildings require specific requirements for the strength and workability of concrete. Aliphatic water reducers can meet these engineering needs, and their relatively low cost can reduce the project’s construction cost.
In constructing the foundation and primary structure of some small industrial plants, aliphatic water-reducing agents can also play their role in reducing water and strengthening, ensuring the quality of the project.
However, in some projects that require high-performance concrete, such as high-performance concrete structures and concrete engineering in unique environments, the performance of aliphatic water reducers may not meet the requirements, and other types of water reducers with better performance need to be selected.
With the continuous development of construction engineering technology, the requirements for concrete performance are becoming increasingly high. Concrete must have high strength and durability and more special functions, such as self-compaction, crack resistance, resistance to chloride ion penetration, self-healing, etc.
This has prompted researchers to continuously explore new water-reducing agents’ research and development direction. They are committed to developing products that meet these high-performance and multifunctional requirements.
Increasing environmental awareness has led to the development of new water-reducing agents, which place greater emphasis on green environmental protection. On the one hand, researchers are striving to find renewable and environmentally friendly raw materials to replace traditional chemical raw materials, reducing resource consumption and environmental impact in the production process of water-reducing agents.
With the increasing diversity and complexity of construction engineering demands, different types of water reducing admixtures have emerged to meet various specific engineering requirements. With today’s rapidly developing technology, these agents will definitely become more diverse, and their performance will improve accordingly.
This article aims to help everyone understand the performance characteristics of different water-reducing agents and ultimately choose the appropriate one.
If you have any new ideas, please discuss them with us!

Super Early Strength Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer For Sleeve Grouting Material
Blog Super Early Strength