
Super Early Strength Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer For Sleeve Grouting Material
Blog Super Early Strength
Blog
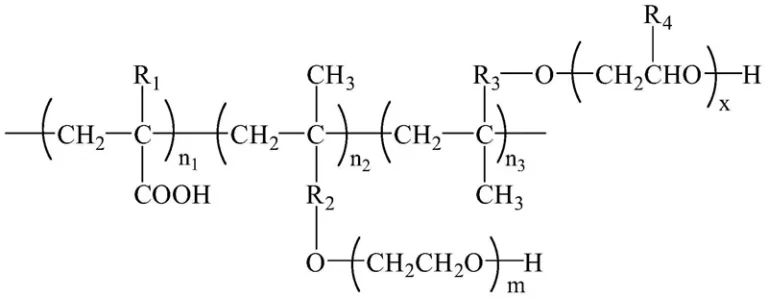
For the PCE superplasticizer synthesis, the design of the molecular structure is crucial, including the main chain groups, side chain density, and side chain length in the molecule. The synthesis methods mainly include in-situ polymerization grafting, polymerization followed by functionalization, and monomer direct copolymerization.
Using polyether as the medium for the unsaturated monomer polymerization reaction, the main chain polymerization and the introduction of side chains are carried out simultaneously.
The process is simple, and the molecular weight of the synthesized water-reducing agent can be controlled to a certain extent.
However, the esterification reaction involved in this method is reversible, and the grafting rate is relatively low when carried out in aqueous solution. This method has gradually been phased out.
This method mainly synthesizes the main chain of the water-reducing agent first and then introduces the side chain for functionalization by other methods.
This method is challenging to operate, and the molecular structure of the water-reducing agent is not flexible. The compatibility between monomers could be better, which significantly limits the use of this method.
This method first prepares active macromonomers and then copolymerizes small monomers and macromonomers in an aqueous solution under the initiation of an initiator.
With the increasingly mature synthesis process and diverse types of monomers, this synthesis method has become the most commonly used method for synthesizing polycarboxylate superplasticizers.

Super Early Strength Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer For Sleeve Grouting Material
Blog Super Early Strength